Percutaneous Electrolysis Therapy (EPTE)
Percutaneous electrolysis therapy (EPTE) is a revolutionary technique used to treat tendinopathies. It uses galvanic micro-currents so that the application is practically painless for the patient. This technique is quite effective: application is quick and patient recovery times are greatly reduced.
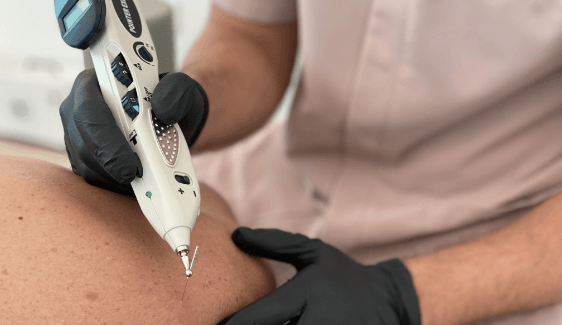
Therapeutic percutaneous electrolysis is an invasive technique that consists of the application of galvanic micro-currents via an acupuncture needle and guided using ultrasound for maximum precision and facilitated access to the injured area of the tendon. The objective is to induce a physical reaction in the tendon, provoking the controlled inflammation necessary to stimulate and activate the body’s self-recovery mechanisms, which by themselves have not been able to regenerate tendon fibers.
In short, it is a technique in which a micro-current is applied via a needle in order to activate the regeneration processes in the injured tissue.
Indicated for all types of patients, EPTE is ideal for elite athletes, but also for other patients who come in with tendon problems.
INDICATIONS
• Degenerative tendinopathy previously assessed with ultrasound:
• Rotator cuff tendinopathy
• Patellar Tendinopathy
• Achilles Tendinopathy
• Epicondylitis
• Epitrochleitis
• Plantar Fasciitis
• Pubalgia
Contraindications
• Clotting problems
• Wounds or scars, tattoos, skin infections
• Lymphadenectomies
• Allergies to metals (nickel)
• Pregnancy
• Fear of needles
• Osteosynthesis
• Heart disease
• Infectious synovitis
• Severe osteoporosis
• Cancer patients
Benefits of Percutaneous Therapeutic Electrolysis (PTEE)
Fast and effective recovery
EPTE accelerates the regeneration of damaged tissues, allowing faster recovery compared to other conventional treatments.
Chronic pain relief
It is particularly effective in the treatment of persistent musculoskeletal pain, such as tendinopathies and long-term injuries.
Minimally invasive technique
The procedure is minimally invasive and virtually painless, minimising discomfort during and after treatment.
Reduction of inflammation
It acts directly on the injured tissue, significantly reducing local inflammation.
Prevention of relapses
By improving the quality of the treated tissue, it reduces the risk of new injuries or relapses in the same area.
Compatible with other treatments
It can be combined with conventional physiotherapy, enhancing its effects and achieving an integral recovery.
Improved sporting performance
Ideal for sportsmen and women who want to recover their physical form quickly without compromising their future performance.
Frequently Asked Questions - Therapeutic Percutaneous Electrolysis
What injuries is TPE indicated for?
TPE (Therapeutic Percutaneous Electrolysis) is effective in treating a variety of conditions, including:
- Supraspinatus tendinopathy.
- Patellar tendinopathy.
- Achilles tendon tendinopathy.
- Epicondylitis (tennis elbow).
- Plantar fasciitis.
- Muscle tears.
- Hamstring injuries.
- Pubalgia.
These are some of the conditions that can benefit from TPE.
Is TPE painful?
TPE is virtually painless. Some patients may experience mild discomfort or a tingling sensation during the procedure, but it is generally well tolerated.
How many TPE sessions are needed to notice improvement?
The number of sessions required depends on the severity of the injury and the patient’s individual response. However, many patients notice significant improvement after 4 to 6 sessions, typically scheduled weekly.
Are there any contraindications for TPE?
Yes, TPE is contraindicated in cases of:
- Presence of prostheses in the treatment area.
- Patients with pacemakers.
- Pregnancy.
- Active oncological processes.
- Thrombophlebitis.
- Skin conditions in the treatment area.
- Neurosensory disorders.
It is essential for the physiotherapist to evaluate each case individually before applying the technique.
What care should I take after a TPE session?
After a TPE session, it is recommended to:
- Avoid intense physical activity for the first 24-48 hours.
- Do not apply ice to the treated area.
- Avoid taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for 24-48 hours after treatment.
- Follow the specific recommendations of your physiotherapist, which may include rehabilitation exercises or gentle stretching.
Does TPE have side effects?
TPE is a safe technique with minimal side effects. Some patients may experience mild inflammation or discomfort in the treated area, which usually resolves within a few hours. It is crucial that the procedure is performed by a trained professional to minimise any risks.
Does TPE replace other physiotherapy treatments?
Not necessarily. TPE is a complementary tool that can be integrated into a broader physiotherapy treatment plan. It is often combined with therapeutic exercises, manual therapy, and other modalities, depending on the specific needs of each patient.
